What is SIBO?Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO) is a condition in which an excessive amount of bacteria end up residing within the small intestine. The bacteria that end up overgrowing are typically a combination of bacteria that are normally found in our gastrointestinal tract. However, they should be populating the large intestine in high numbers, and not the small intestine.
Our intestines are divided into two groups – the small intestine, and the large intestine. Food is broken down into its simple, absorbable components in the small intestines, while the waste is pushed into the large intestine for eventual evacuation during bowel movements. Normally, about 98% of our gastrointestinal bacteria are meant to reside in our large intestine, while only about 2% in our small intestine. In SIBO, much more than 2% are residing in the small intestine, and this creates havoc in our digestive processes. |
How does SIBO cause IBS?
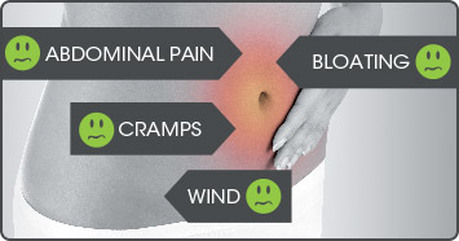
The majority of bacteria in our gastrointestinal system feed on fibers and certain sugars such as lactose (milk sugar) and fructose (fruit sugar). When the bacteria feed, they immediately begin to produce gases such as hydrogen and methane. If SIBO is present, there ends up being an excessive amount of hydrogen and/or methane gases being produced within the small intestine, which leads to the following symptoms as the small intestines expand:
- Abdominal bloating/distension
- Excessive belching
- Excessive flatulence
- Abdominal pain/cramping
- Diarrhea or constipation or alternating between both
- Nausea
- Heartburn
What Conditions May Be Related to SIBO?
As a common underlying cause, SIBO is associated with many other health complaints and conditions. SIBO is either correlated with causing the conditions below, or is thought to be partly caused by these conditions. The list may be large, but if you experience digestive disturbances and one or more of the conditions listed, SIBO testing is warranted. By treating the root cause, patients can experience a permanent shift in their health.
|
|
|
Phases of SIBO Treatment Include:
PreparationThis phase of treatment involves first testing for SIBO causing bacteria using a 3-Hour Breath Test to determine the extent of the dysbiosis and specific types of bacteria involved. We then begin by supporting the body to be able to eliminate toxins produced by the SIBO causing bacteria.
|
EradicationAfter learning which types of bacteria are present in the small intestine, we can target anti-microbial treatment to those bacteria. Often a combination of conventional antibiotics and herbal antimicrobials are used to eradicate the pathogenic bacteria.
|
Maintenance
We address the causes of why you may have the overgrowth in the first place. This may be due to low stomach acid, poor liver or gallbladder function, dietary choices or prescription drug use We also stimulate the digestive tract to move in a coordinated fashion during this period of time
|